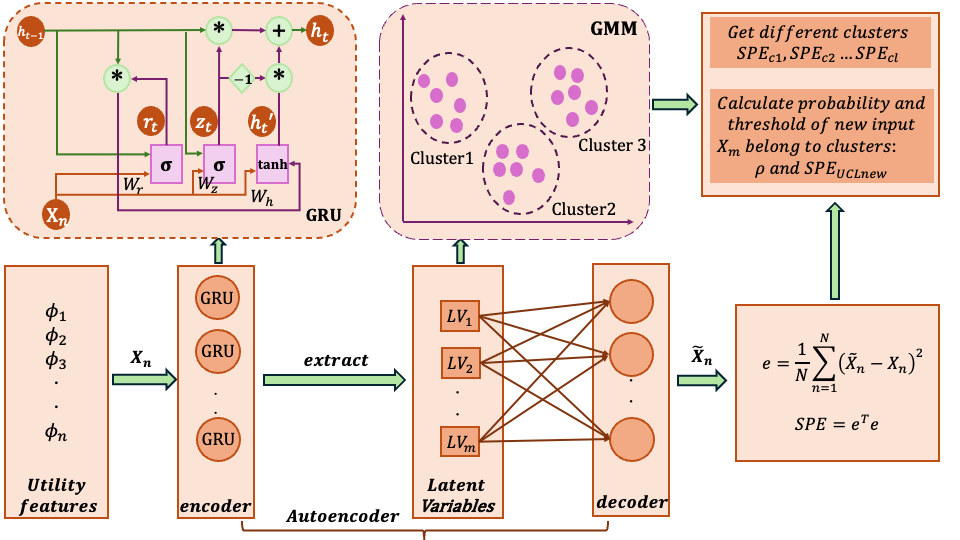
Abnormal driving behaviors pose major safety risks, with about 94% of crashes preventable through early detection. Existing methods often ignore driver heterogeneity, dynamic contexts, and vehicle interactions, and are limited by scarce ground-truth labels. This paper proposes an unsupervised anomaly detection framework, Utility-Enhanced GRU-AE-GMM, combining utility-based risk modeling with deep learning. Utility functions capture safety-related risks, while a GRU AutoEncoder learns temporal driving patterns. Latent representations are clustered with a Gaussian Mixture Model(GMM) to set adaptive thresholds and interpret anomalies. Experiments on the HighSim dataset demonstrate effective detection, with anomalies aligning with spikes in interpretable utility features.